目录
| Folien | Chapter | Video | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SIMD | 05 | 2.3.1 - 2.3.7 | |
SIMD
Single Instruction Multiple Data: Same instruction is performed on multiple data elements
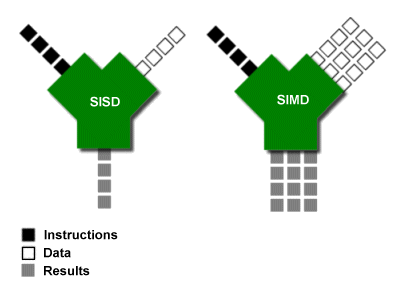
Motivation
Multimedia applications:
-
process small data types: (8 -16 bit) image/audio/video
much narrower than 64-bit data word of modern processors
-
contain fine-grain Data-level Parallelism (DLP):
same operation is performed on multiple data elements
Register File
- 在MIPS64标准下的整数寄存器和浮点数寄存器是64位(8字节)的
- 不同标准下的SIMD拓展的长度是不同的
- 目的是在一个寄存器里存入多个数据
- 比如假定128位的拓展
- 就可以存入8个halfword(16位),或者4个word(32位),或者4个Float(32位),2个Double(64位)等
- SIMD可以映射到已存在的Reg(比如由两个整数寄存器组成等), 现今比较常见的是用单独的寄存器。
Add
-
64位拓展下的加法指令
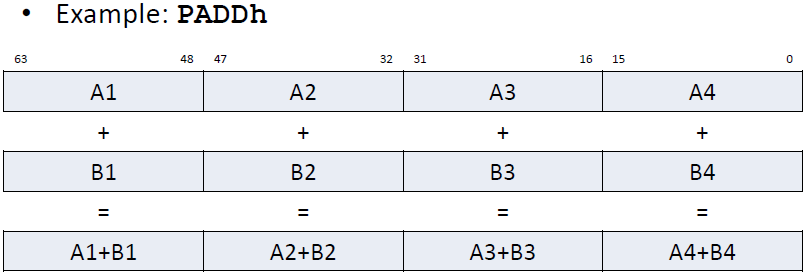
-
实现:与普通加法的区别在于 A4+B4的进位 不用传递到 A3+B3
-
加法的问题:溢出 → (Clipping/saturation):
比如在图片处理中RGB下黑色(0,0,0),白色(255,255,255)
-
如果溢出 模运算(Modular arithmetic)
(234,235,236) + (22,23,24) = (0,2,4) 导致:很亮->很暗
-
或者 饱和运算(Saturation arithmetic) / Clip
(234,235,236) + (22,23,24) = (255,255,255)
-
-
signed Saturation: [-128, 127]
unsigned Saturation: [0, 255]
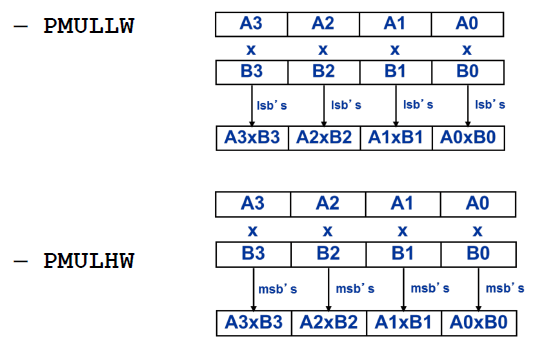
Multiplication
- 乘法的问题:

-
解决方法:
-
选择low- or high-order parts
-
Reduction: Multiply-Add Operation
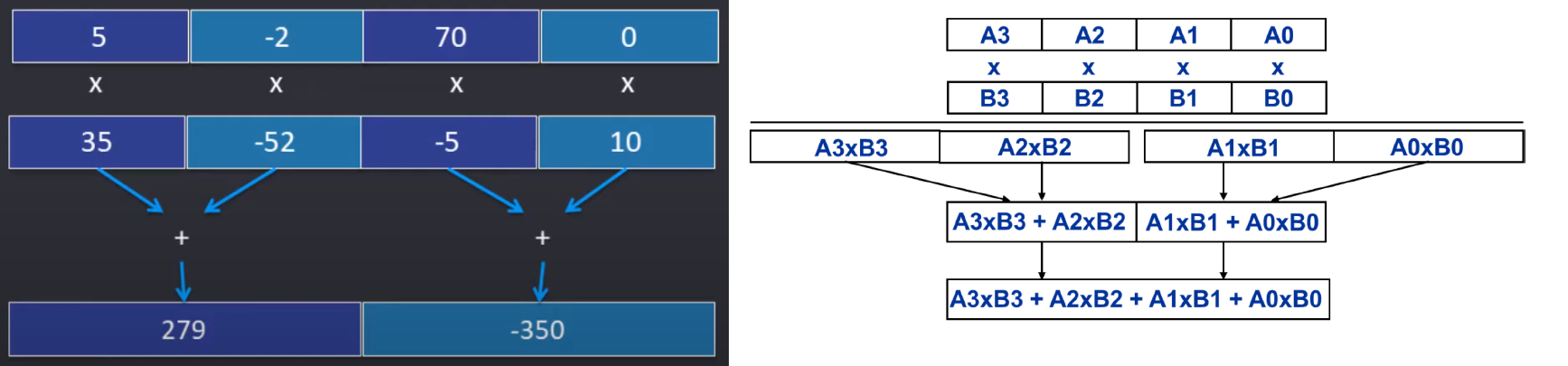
-
Wider Result Reg
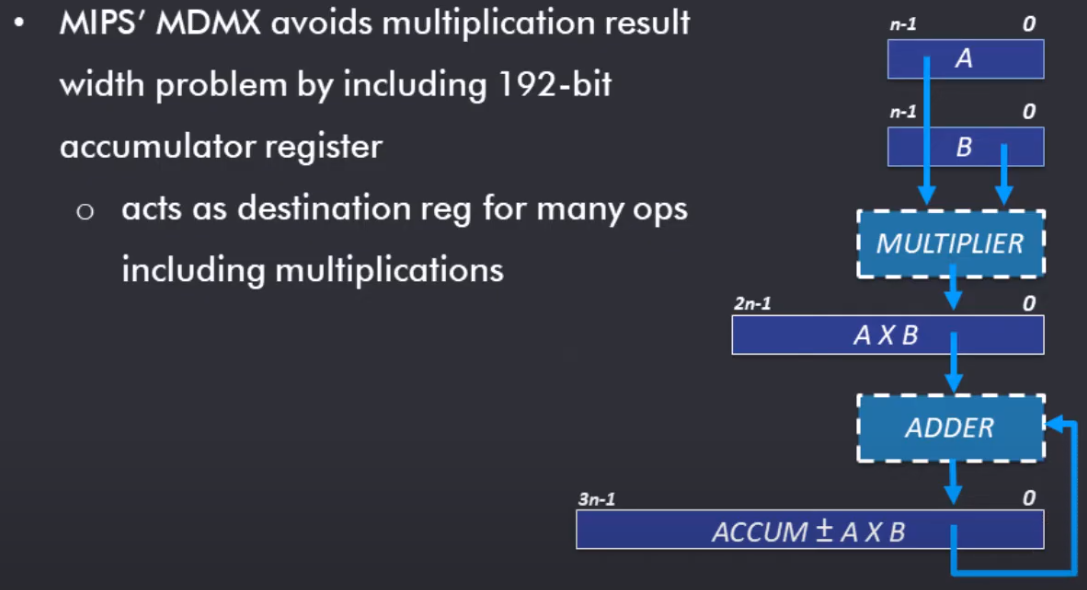
-
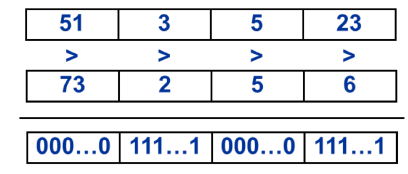
Compare
- 以每个Pack为单位进行比较
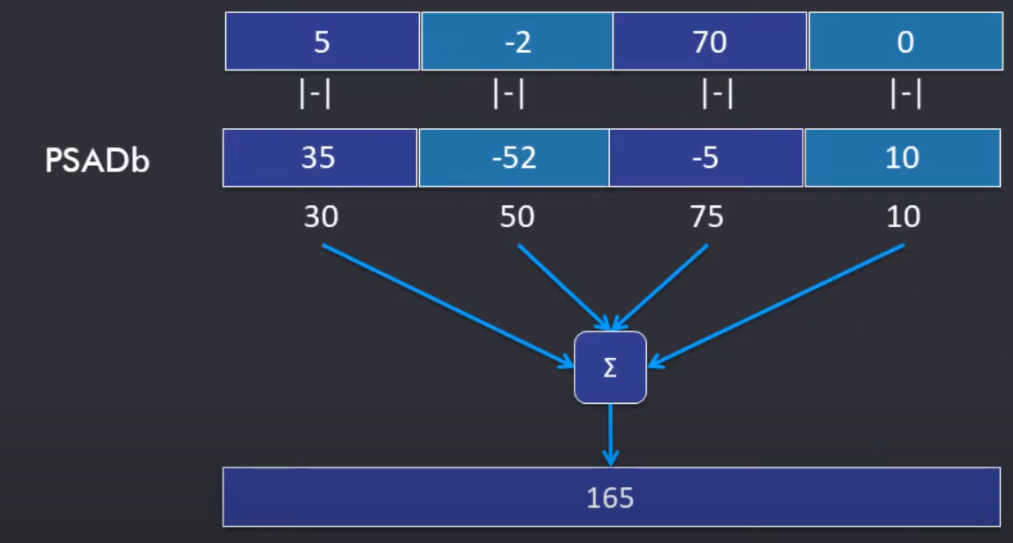
Special Purpose Instruction
比如:
Sum of Absolute Differences
-
专门设定这个操作的原因:
to accelerate Block_Match() video coding kernel(consumes up to 70% of time of MPEG coding)
Conversion
-
原因:
计算时需要精度大,保存时精度小一点就够了。计算过程中会有精度损失。比如加和求平均 103+105超过128的精度了,但均值104是在精度内的。
pack/unpack:
-
pack: from wider to narrower data types
- truncation: high-order bits are ignored
- saturating: clipped to the range of smaller data type
-
unpack: from narrower to wider
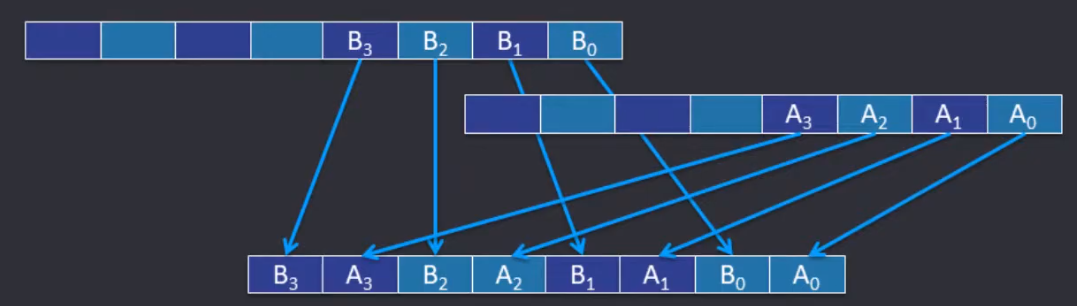
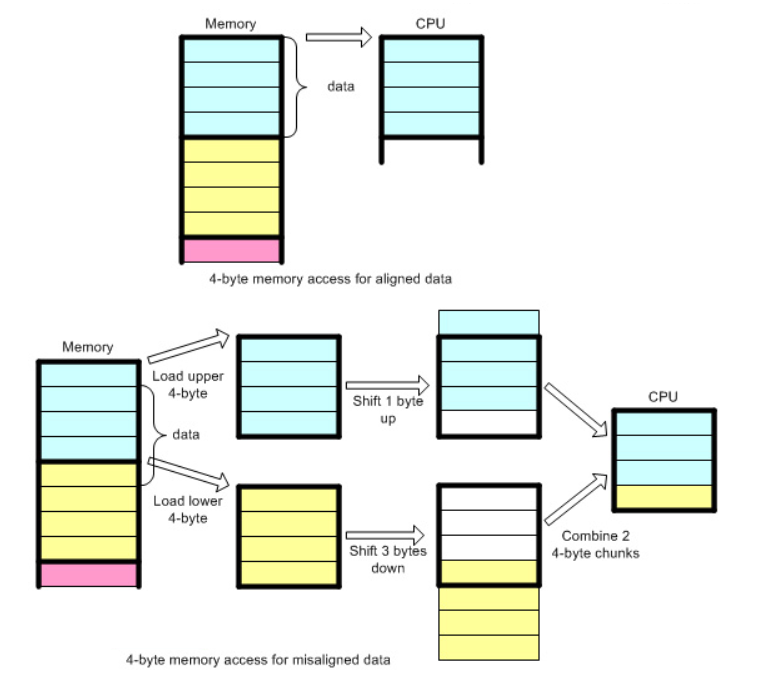
Data Alignment
对齐
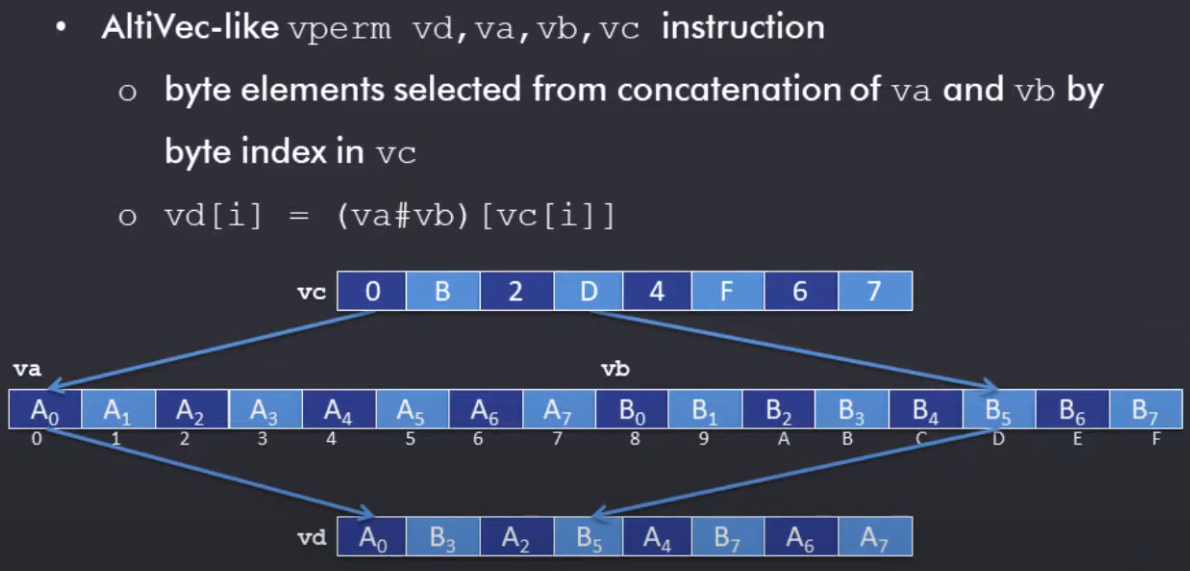
Data Reordering
- Permute
- 任意排序
- most powerful, most costly
- Mixing / unpacking / merging
- 交替排序
- 同Conversion中的unpacking
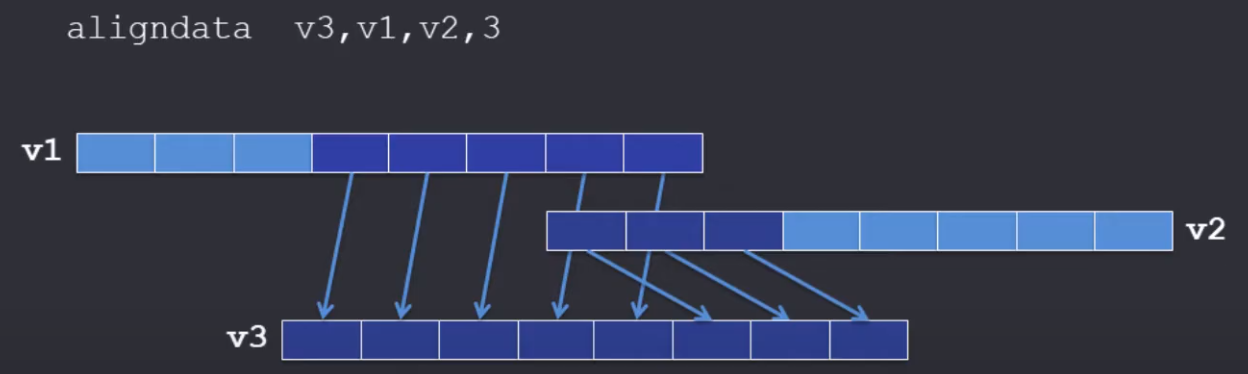
- Align / Rotate
- 不能改变排序,只是按顺序截取并组合
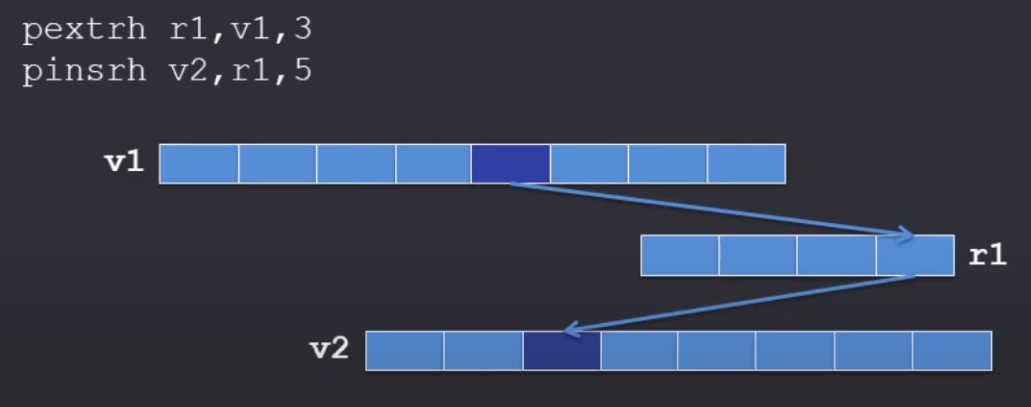
- Insert / extract
- 提取插入
Control Flow
数据集并行遇到 if loop 会很麻烦,比如循环求绝对值,解决方法:
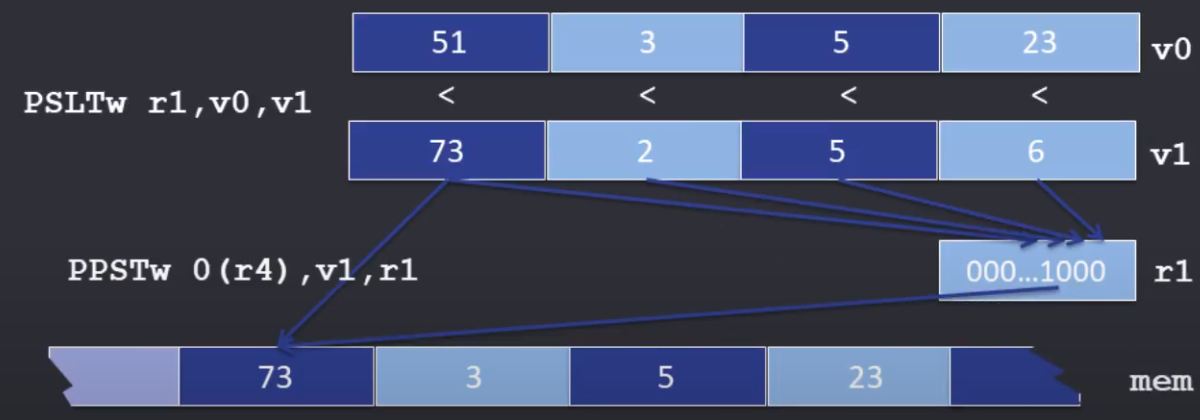
- element masks
- comparison的结果就是element mask
- masks和 按位与/或等逻辑操作 结合, 达到特定的效果
- bit masks
- element mask 对每个element是位数相同的一串1/0。bit mask用一个1/0。
- 通过partial stores,对对应位覆盖。