基于 Prof. Andrea Cominola 参与的论文[1][3][4]
Water Metering
Basic Comparison
- traditional Water meter
- low-frequency reading
- coarse resolution m³
- Different types:
- Mechanical flow meters
- Magnetic flow meters
- Ultrasonic flow meters: 管道外测量
- smart meter
- data resolution up to 72 pulses/L
- data sampling frequency and logging 5-10s
Benifits of Smart Water Meter [2]
- automate meter reading
- improved demand and revenue forecasting
- establish leak alerting
- establish a detailed customer data portal
- offer monthly billing
- establish detailed water balancing
- establish a capability for data analytics
- increase knowledge of coustomers and assets
WDMS water demand management strategies
Benefits and challenges of using smart meters for advancing residential water demand modeling and management [4]
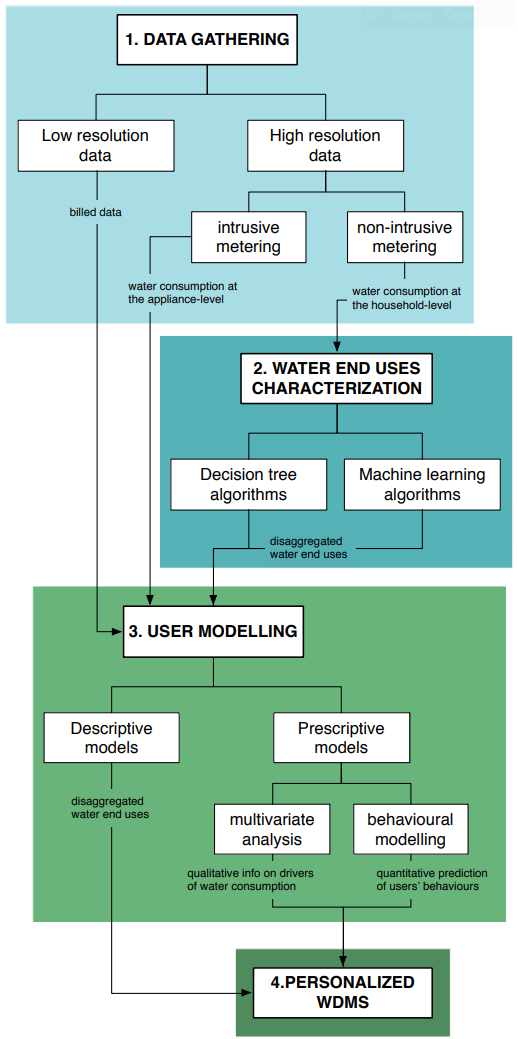
challenges in use
- Hardware VS Software potential/limitation
- HW: 长期稳定的设备 等
- SW: analysis data, commuication …
- Big Data management
- Privacy and intrusiveness
- Cybersecurity
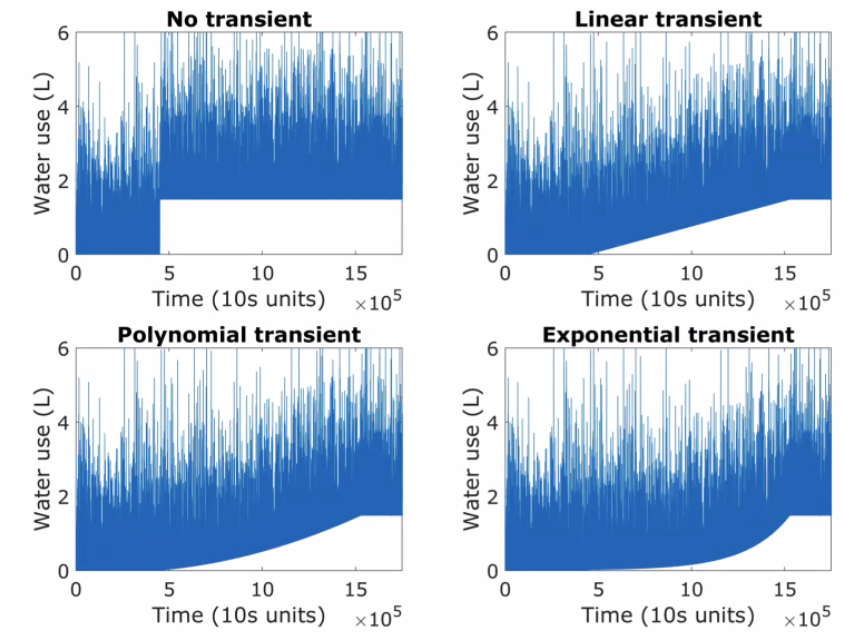
Implications of sampling frequency on water applications
Implications of data sampling resolution on water use simulation, end-use disaggregation, and demand management [1]
Sampling Frequency
10s, 1min, 5min, 15min.1h, 1d …
Implications
-
Water end-use disaggregation
-
One Measure → Many End-Uses (Toilet/Shower/Garden/…) 一个预测多分类任务
-
指标:
-
individual appliance usage
-
individual appliance pattern
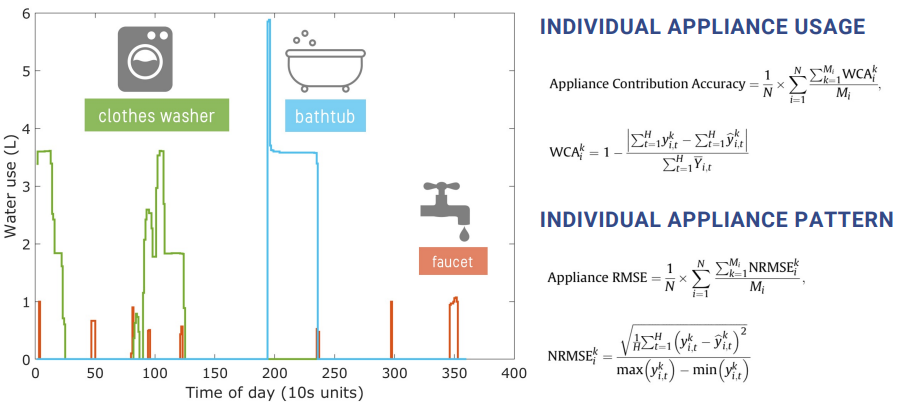
-
-
-
Leakage detection
-
Leakage 种类
-
指标:
-
Average Water Loss
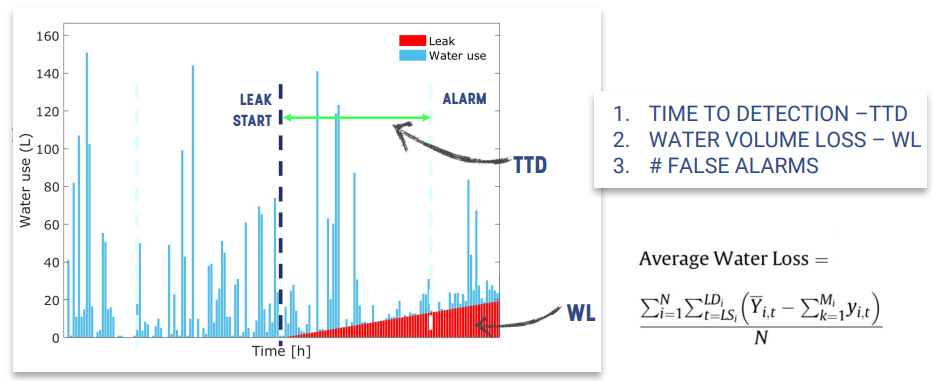
-
-
-
Peak demand estimation
- Measuring frequency

-
指标:
-
Peak Estimation Error
-
Peak Estimation Time Gap
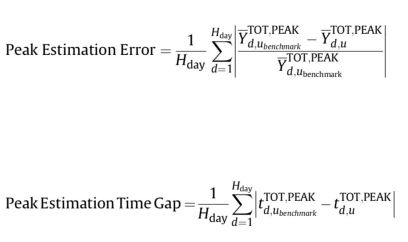
-
-
Cost
- 指标:
- Data Storage ( MB/(Household * Year) )
- 指标:
-
Feasibility
- 指标:
- Commercial availability
- 指标:
Data
-
generation using STREaM
- 5 Indoor fixtures were used (toilet, washmachine, shower, dish washer, faucet)
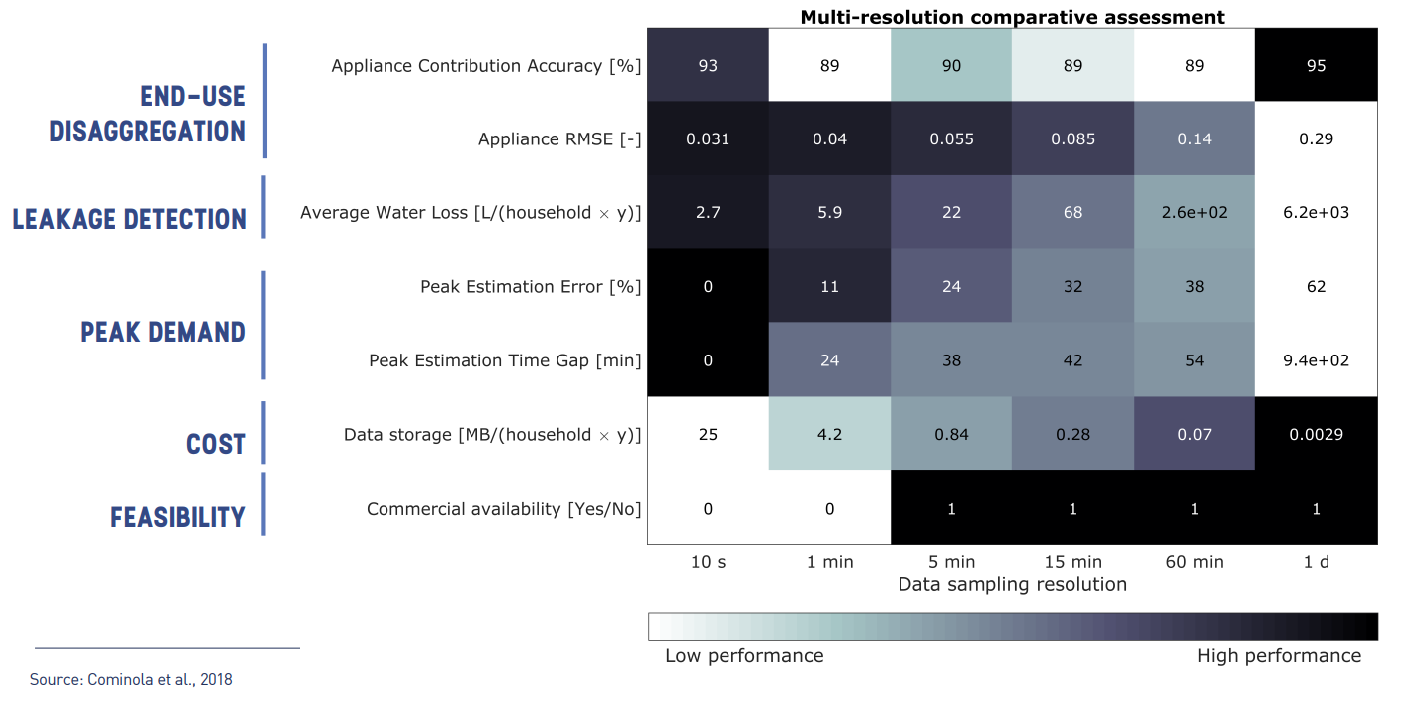
- Summary
- Data sampled with < 5 min resolution seem to be:
- Beneficial for different purposes (leak detection, peak estimation, end use disaggregation)
- Not easy to get with commercial products
A multi-utility vision Water+Electricity
水消耗和电力消耗的联系:城市和个人
Integrated intelligent water-energy metering systems and informatics [3]
[1] Abdallah, Adel & Cominola, Andrea & Giuliani, Matteo. (2018). Implications of data sampling resolution on water use simulation, end-use disaggregation, and demand management. Environmental Modelling and Software. 102. 10.1016/j.envsoft.2017.11.022.
[2] Monks, Ian, Rodney A. Stewart, Oz Sahin, and Robert Keller. (2019). Revealing Unreported Benefits of Digital Water Metering: Literature Review and Expert Opinions Water 11, no. 4: 838.
[3] Stewart, Rodney & Nguyen, Khoi & Beal, Cara & Zhang, Hong & Sahin, Oz & Bertone, Edoardo & Vieira, Abel & Castelletti, Andrea & Cominola, Andrea & Giuliani, Matteo & Giurco, Damien & Blumenstein, Michael & Turner, Andrea & Liu, Ariane & Kenway, Steven & Savic, Dragan & Makropoulos, Christos & Kossieris, Panagiotis. (2018). Integrated intelligent water-energy metering systems and informatics: Visioning a digital multi-utility service provider. Environmental Modelling and Software. 105. 10.1016/j.envsoft.2018.03.006.
[4] Cominola, Andrea & Giuliani, Matteo & Piga, Dario & Castelletti, Andrea & Rizzoli, Andrea-Emilio. (2015). Benefits and challenges of using smart meters for advancing residential water demand modeling and management: A review. Environmental Modelling & Software. 72. 198 - 214. 10.1016/j.envsoft.2015.07.012.